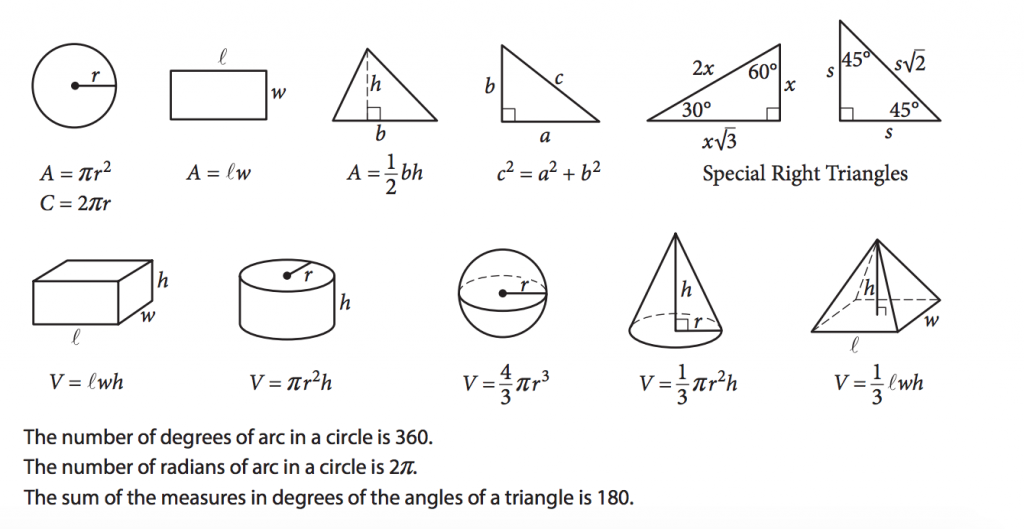
The SAT formula sheet provides basic formulas for circles, area, triangles, and volume. But there many additional formulas it will be helpful to know on test day so you can fly through the math section with confidence.
Problem Solving and Data Analysis
Percents

OR change words to an algebraic equation and solve
Example: 40% of what is 20?

Percent increase or decrease:

Mean (the average)

Median
Middle value when items are arranged from least to greatest
Range
The difference between the max value and min value
Mode
Value that occurs the most in a set
Standard Deviation
Shows how spread data points are.
Low standard deviation: data points are closer to the mean
High standard deviation: data is spread over a wider range
Probability of an Event

Joint or conditional probability

Mutually exclusive probability

Fundamental Counting Principle
Pick 1 from each group, multiply the number of options in each group
Permutation
A combination of events occurring when order matters and the items cannot be repeated

Combination
A combination of events occurring when the order does NOT matter

Arithmetic Sequences
Each term (t) is the previous term plus a common difference (d)
to find the nth term:

Geometric Sequences
Each term (t) is the previous term times a common ratio (r)
to find the nth term:

Key Math Section Strategy for the ACT or SAT
Heart of Algebra and Passport to Advanced Math
Domain
Set of possible values of x that can be plugged into a function (Input).
Range
Set of possible values of y that a function takes on (Output).
Lines
Slope of the line:

Parallel lines have the same slope and Perpendicular lines have slopes that are negative reciprocals
Slope-intercept form:

Point-slope form:

Midpoint Formula

Distance Formula

Direct Variation
y=kx where k is the constant of variation
Indirect Variation

where k is the constant of variation
Standard Form of a Quadratic

To find the solutions: set y equal to 0, and solve for x by factoring or use the Quadratic Formula

To find the vertex:

plug value back into the equation to find y-coordinate
Vertex Form of a Quadratic

The vertex is (h, k).
Factored Form of a Quadratic

x-intercepts/solutions/zeros are x=p & x=q
Exponential Functions

Shows growth if b>1or decay if 0<b<1
Growth/Decay when r is a percent:


Interest compounded n times for t years:

Exponents & Roots
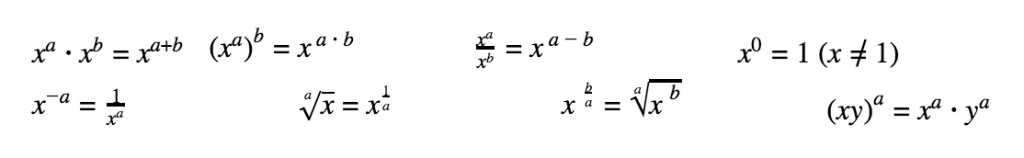
Additional Topics in Math
Complex Numbers

Use the conjugate to eliminate the imaginary:

Triangles

Degrees sum to 180°
Sides: No side can be greater than the sum or less than the difference in length of the other two. Side lengths are in the same ratio as opposite angle measures
Special Right Triangles




Complementary angles sum to 90°
Supplementary angles sum to 180°
Exterior angles for ANY polygon sum to 360°.
Interior angles for a polygon sum to 180°(n-2) where n is the number of sides in the polygon.
Trigonometric Ratios

Trigonometric Relationships

Circle

Degrees in a Circle:

Find radians of given degrees:

Find degrees of given radians:

Standard Form of a Circle:

Vertex Form of a Circle:

where (h,k) is center and r is radius
Rectangular Prism

Cylinder
